In recent months, several European Union and European Economic Area (EU/EEA) member states and neighboring countries have reported an increase in the number of pertussis cases compared to the pre-Covid-19 pandemic period. According to data available from ECDC, the most affected age groups are children and younger adolescents. In addition, infants and young children who are too young to receive the required vaccination course are also affected.
Infants are at the highest risk of severe illness and death from pertussis, and in the EU/EEA countries, almost all deaths have been in this age group – infants under 3 months of age. That’s why especially important to vaccinate pregnant women against whooping cough during pregnancy, as it also gives a significant protective effect to the child until he has reached the age of vaccination. Babies should receive the first vaccine against pertussis at the age of 2 months according to the vaccination calendar. Publicly paid pertussis vaccination is available for pregnant women.
The situation in Latvia
Latvian epidemiological surveillance data show that in 2024, 155 cases of pertussis were registered from January to March, and in 2023, 21 cases were registered in January-March (a total of 111 pertussis cases were registered in 2023).
The highest incidence in 50 years was observed in 2019, when 720 cases of whooping cough were registered (37.5 cases per 100,000 inhabitants), the trend of increasing incidence is also currently observed. A pronounced increase in the number of pertussis began in December 2023, when the number of registered patients exceeded the number of patients in December 2022 by 4.3 times. Periodic increases in incidence are associated with an increase in the number of people susceptible to infection. As the spread and intensity of circulation of the pathogen in the community increases, the risk of infection also increases for babies who have not yet been vaccinated or who have not completed the course of primary vaccination against pertussis and are therefore particularly susceptible to this very serious infection. Thus, it is very important to start vaccination on time and follow the vaccination schedule.
According to the current vaccination calendar for children, the vaccine against pertussis should be received at the age of 2, 4, 12-15 months, 7 and 14 years, by vaccination with the combined vaccine against pertussis, diphtheria, tetanus and poliomyelitis, Haemophilus influenzae type b and hepatitis B (2 , 4, at 12-15 months), the combined vaccine against whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus and poliomyelitis (at the age of 7) or the combined vaccine against whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus (at the age of 14).
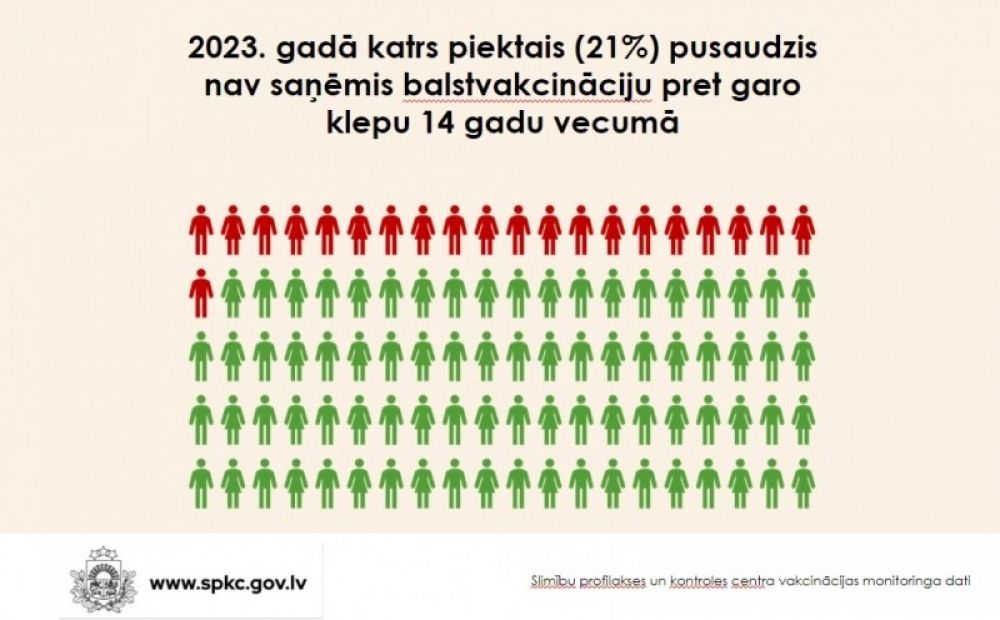
Currently, compared to the pre-pandemic period, the number of unvaccinated children who have not received the pertussis vaccination between the ages of 7 and 14 has significantly increased.
As part of the Immunization Week, SPKC reminds parents to take an active interest in and regularly monitor the vaccination data in their and their child’s Vaccination Passport and vaccination calendar instructions, and at the specified times apply yourself or apply for the child’s vaccination at the family doctor.
In recent months, several European Union and European Economic Area (EU/EEA) member states and neighboring countries have reported an increase in the number of pertussis cases compared to the pre-Covid-19 pandemic period. According to data available from ECDC, the most affected age groups are children and younger adolescents. In addition, infants and young children who are too young to receive the required vaccination course are also affected.
Infants are at the highest risk of severe illness and death from pertussis, and in the EU/EEA countries, almost all deaths have been in this age group – infants under 3 months of age. That’s why especially important to vaccinate pregnant women against whooping cough during pregnancy, as it also gives a significant protective effect to the child until he has reached the age of vaccination. Babies should receive the first vaccine against pertussis at the age of 2 months according to the vaccination calendar. Publicly paid pertussis vaccination is available for pregnant women.
Vaccination in Latvia against whooping cough was started in 1958. The total number of cases of illness in the 5 years before the start of vaccination was 27367, but in 2019-2023. in 1228. The reduction in the number of cases from the start of vaccination is 95.5%.
Whooping cough is highly contagious, an acute respiratory infectiona, which is called Bordetella pertussis a rod-shaped bacterium. The disease is characterized by a severe, paroxysmal cough that can last for two months or even more. Before the start of vaccination (in 1958), whooping cough was a very widespread disease, which mainly affected children under 5 years of age, mostly under 1 year of age. Currently, the highest morbidity is observed adolescents, children up to one year of age and young adults.
Whooping cough is highly contagious, an acute respiratory infectiona, which is called Bordetella pertussis a rod-shaped bacterium. The disease is characterized by a severe, paroxysmal cough that can last for two months or even more. Before the start of vaccination (in 1958), whooping cough was a very widespread disease, which mainly affected children under 5 years of age, mostly under 1 year of age. Currently, the highest morbidity is observed adolescents, children up to one year of age and young adults.
Tags: incidence whooping cough increasing Latvia
-