Biologists call animals living alongside humans synanthropic. Synanthropus (from Greek syn – together and anthròpos – person) in translation means: one who is next to a person. So a creature that has adapted to life in close proximity to humans in landscapes significantly modified by humans.
Classic synanthropes are sparrows. They can be found in cities of various sizes, on the outskirts of large cities, as well as in populated areas in rural areas – villages, abandoned homesteads and farms.
Sparrows have learned to build their nests in all kinds of voids, for example, in building niches, cracks, ventilation pipes, under roof slates, tiles, tin, also in tree cavities, very often in bird cages of various sizes, old warblers’ nests, piles of white stork nests and many other places. . In Latvia, sparrows are seen hatching their offspring two or three times a season.
These birds are quite common here. Still common, but noticeably less often than in the past, because sparrows need from people, first of all, not a place for nesting, as it might seem, but rather easily obtainable food. The necessary food for these birds is available where people take care of the land in a variety of ways, keep livestock freely, where people do not throw everything they don’t eat into tightly closed garbage containers. We have fewer and fewer such places.
Visually, sparrows, where they still live, are usually recognized among other birds by their relatively inconspicuous gray-brown or grey-brown primary plumage. They are also characterized by a relatively small tail, short legs and a rather massive beak.
Acoustically, the presence of these birds is conveyed by the characteristic collective chirping. Sparrows are social animals – they stay and chirp in flocks or at least in groups.
It is significant that three different feathered sparrows live in Latvia. Let’s get to know them!
House sparrow the male is the largest of our sparrows – it is significantly different from the female.
The male house sparrow has a dark gray top of the head, chestnut-brown upper side of the head, gray-white cheeks, as well as a black area under the beak and on the neck (during the breeding season it also appears on the upper chest, but then disappears from the chest, remaining only on the neck). Black, elongated spots surround the eyes of the bird. From a short distance, two small, white spots are visible on both sides of the head – one above the eye, the other behind the eye. The female does not have all these mentioned signs.
A male house sparrow.
Photo: A frame from the video
The color of the plumage on the upper side of the wings is basically brown, with black barring and a white crossbar. The feathers of the back and the underside of the torso are light gray. Black tinted tail.
The eyes of the animal are dark brown, the beak is black during the breeding season, then turns brown.
A female house sparrow is slightly smaller than the male. As already mentioned, she does not have the multicolored decoration on her head and on her chest. The top of the head is brown in the female. Elsewhere, where the coloration of the two sexes does not differ significantly, the body plumage of the female is however less bright than the plumage of the male.
A female house sparrow.
Photo: A frame from the video
The female house sparrow is characterized by a light, broad eyebrow stripe, however, it is indistinct, dull. The eyes of the female are brown. The beak is also brown, but with a pale yellow base.
Outside the breeding season, the costume of birds is more inconspicuous, lighter. Airplanes look more shabby.
The young individuals of both sexes of the house sparrow (as is characteristic of many other species of birds) for some time look very much like the females, but their plumage is duller and there are no black tones in their coloring.
So, two externally different sparrows have already been considered – a male house sparrow and a female house sparrow. Who is the third?
To answer, you need to look at a representative of another, related, slightly smaller species – the field sparrow.
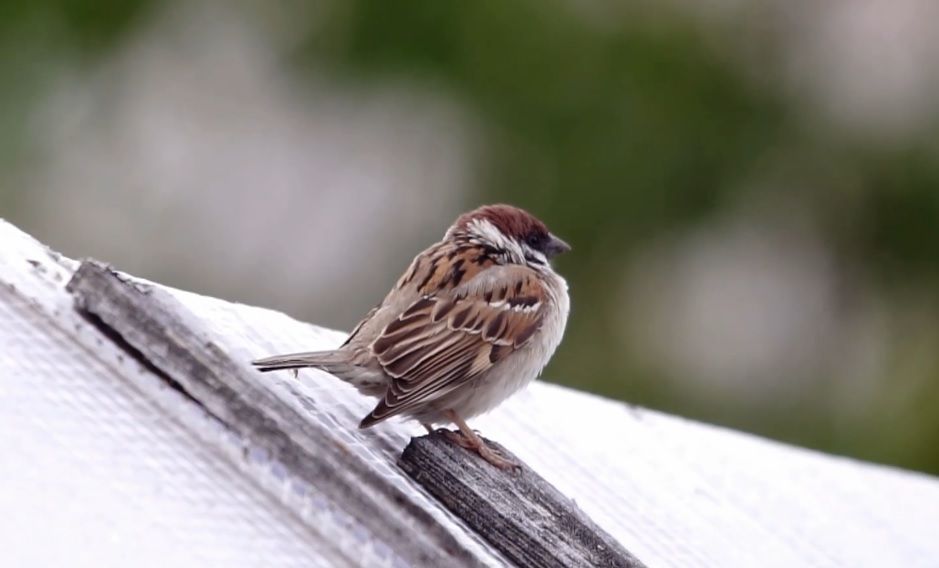

Field sparrow.
Photo: A frame from the video
Field sparrows of both sexes look somewhat similar to male house sparrows at first glance.
It is important that this species, unlike the house sparrow, does not have a pronounced sexual dimorphism, that is, the plumage of the male and female is the same. Seasonal external changes are also insignificant.
The top of the country sparrow’s head is light chestnut brown, with a small but striking black crescent-shaped spot on the white cheeks. A clearly visible, relatively wide, snow-white band stretches around the bird’s neck. There is a small black area under the beak. The plumage on the upper side of the wings is brown, with black markings and two light cross-stripes. The lower part of the body is basically pale grey, with an ocher shade on the sides. The eyes of the country sparrow are dark brown, the beak is dark gray or black. The coloring of young birds is duller than that of old birds.
So different sparrows: a male house sparrow, a female house sparrow, and a field sparrow of either sex. With food in generous places, everyone can be seen in one place.